Blog Time Plugin
Display the time according to your blog via an admin toolbar widget, a sidebar widget, and/or a template tag.
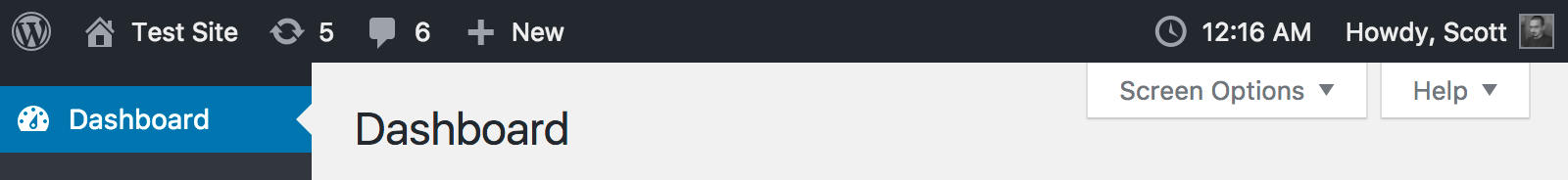
This plugin adds a dynamic, functional clock to the admin bar (at top of all admin pages) to show the server time for the blog. The clock automatically updates as time passes, as you would expect of a digital clock.
This plugin also supports a static mode which puts a timestamp string at the top of all admin pages instead of the dynamic clock. This static admin time widget can be clicked to update the time in-place (without a page reload) to show the new current server time.
Also provided is a “Blog Time” widget providing the same functionality as the admin widget, but for your sidebars. You may also utilize the plugin’s functionality directly within a theme template via use of the template tag c2c_blog_time().
NOTE: For the front-end widget, if the “Use dynamic clock?” configuration option is unchecked, this plugin generates a timestamp and NOT a clock. The time being displayed is the time of the page load, or if clicked, the time when the widget last retrieved the time. It won’t actively increment time on the display. By default the widget displays a dynamic clock that does increment time.
This is most useful to see the server/blog time to judge when a time sensitive post, comment, or action would be dated by the blog (i.e. such as monitoring for when to close comments on a contest post, or just accounting for the server being hosted in a different timezone). Or, when used statically as a timestamp and not a clock, it can indicate/preserve when the page was loaded.
Thanks to Moment.js for the JavaScript date handling library.
Links: Plugin Homepage | Plugin Directory Page | GitHub | Author Homepage
Template Tags
The plugin provides one template tag for use in your theme templates, functions.php, or plugins.
Functions
<?php function c2c_blog_time( $time_format = '', $echo = true ) ?>
Returns and/or displays the formatted time for the site.
Arguments
$time_format(string)
Optional. PHP-style time format string. See https://www.php.net/manual/en/datetime.format.php for more info. Default is ” (which, unless otherwise modified, uses the default time forat: ‘g:i A’).$echo(bool)
Optional. Echo the template info? Default is true.
Examples
<?php // Output the site's current time.
c2c_blog_time();
?><?php // Retrieve the value for use in code, so don't display/echo it.
$site_date = c2c_blog_time( 'M d, Y', false );
?>
Hooks
The plugin exposes four filters for hooking. Code using these filters should ideally be put into a mu-plugin or site-specific plugin (which is beyond the scope of this readme to explain). Less ideally, you could put them in your active theme’s functions.php file.
c2c_blog_time (filter)
The 'c2c_blog_time' hook allows you to use an alternative approach to safely invoke c2c_blog_time() in such a way that if the plugin were deactivated or deleted, then your calls to the function won’t cause errors in your site.
Arguments:
- same as for
c2c_blog_time()
Example:
Instead of:
<?php c2c_blog_time(); ?> Do:
<?php echo apply_filters( 'c2c_blog_time', '' ); ?> c2c_blog_time_format (filter)
The 'c2c_blog_time_format' hook allows you to customize the default format for the blog time. By default this is ‘g:i A’ (though this may be different if modified by localization).
Arguments:
- $format (string): The default format for the blog time.
Example:
/** * Change the default blog time string * * @param string $format The default time format. * @return string */ function change_blog_time_format( $format ) { return 'b, g:i A'; } add_filter( 'c2c_blog_time_format', 'change_blog_time_format' ); c2c_blog_time_toolbar_widget_for_user (filter)
The c2c_blog_time_toolbar_widget_for_user hook allows you to control if the admin toolbar clock widget should be shown, on a per-user basis. By default the admin toolbar clock is shown to everyone who can see the admin toolbar.
Arguments:
- $shown (boolean): Whether the admin toolbar clock widget should be shown. Default of true.
Example:
/** * Only show the admin toolbar clock for the 'boss' user. * * @param $show bool Status of whether the admin toolbar clock should be shown. * @return bool */ function restrict_blog_time_widget_appearance( $show ) { return 'boss' === get_current_user()->user_login; } add_filter( 'c2c_blog_time_toolbar_widget_for_user', 'restrict_blog_time_widget_appearance' ); c2c_blog_time_active_clock (filter)
The 'c2c_blog_time_active_clock' hook returns the boolean value indicating if the Javascript-powered dynamic clock introduced in v2.0 should be enabled or if instead the v1.x era behavior of a static timestamp that can be clicked to update the timestamp via AJAX should be enabled. By default the dynamic clock is enabled.
Arguments:
- $allow (boolean): Boolean indicating if the admin widget should be a dynamic clock. Default is true.
Example:
// Disable the dynamic clock and use the static timestamp (whcih can be clicked to update the time via AJAX) instead. add_filter( 'c2c_blog_time_active_clock', '__return_false' ); Installation
- Install via the built-in WordPress plugin installer or download and unzip
blog-time.zipinside the plugins directory for your site (typicallywp-content/plugins/) - Activate the plugin through the ‘Plugins’ admin menu in WordPress
- Optional: Customize the time format used for displaying the time via the “Blog Time Format” setting found in Settings -> General.
- Optional: Use the ‘Blog Time’ widget or the template tag
c2c_blog_time()in a theme template file to display the blog’s time at the time of the page’s rendering.
Screenshots
FAQ
Under the site’s general admin settings — at Settings -> General — you’ll find a “Blog Time Format” setting that accepts any valid PHP time format token. See https://www.php.net/manual/en/datetime.format.php for more information regarding valid time format tokens.
The widget and template tag also allow you to specify a time format directly.
The default value for the time format, and the one used by the display of the blog time in the static admin widget, can be overridden by hooking the c2c_blog_time_format filter and returning the desired time format. This takes precedence over the setting’s value.
The widget’s “Use dynamic clock?” configuration setting may not be checked (which it is by default). Or JavaScript could be disabled in the browser.
Your machine may well be synced with the server’s clock. One test you can perform is to change the blog’s time zone (under Settings -> General). The blog’s time will then be set to a different hour, which should then be reflected by the widget. Remember to change the time zone back to its proper value!
Yes, but only programmatically at the moment. Check out the docs for the 'c2c_blog_time_toolbar_widget_for_user' filter for more information and a code example.
See the Filters section for the 'c2c_blog_time_active_clock' filter, which includes an example line of code you’ll need to add to your theme.
Via Settings -> General, you can set the “Blog Time Format” value to something like M d, Y, which results in a time format like “Jun 21, 2021”. See https://www.php.net/manual/en/datetime.format.php for other month, day, and year time format tokens.
Yes.
Changelog
4.0.1 (2021-07-29)
- Fix: Ensure inline script is only output once per pageload to prevent issue when blog time appears on page multiple times, which resulted in all acting as if static
- New: Add
reset()to restore memoized class variables to default values - Change: Note compatibility through WP 5.8+
4.0 (2021-06-19)
Highlights:
This recommended release introduces a setting for configuring the blog time format, adds support for the ‘T’ timezone format token, updates the bundled Moment.js library, improves documentation, restructures unit test files, notes compatibility through 5.7+, and incorporates numerous behind-the-scenes tweaks.
Details:
- New: Add setting for configuring time format
- New: Add “Blog Time Format” setting to the “General Settings” page.
- New: Add link to setting from plugin’s action links
- New: Show default time format when setting is blank
- New: Show inline notice below setting when time format is filtered, and indicate that it takes precedence over setting
- New: Add
initialize_setting(),allowed_options(),display_option(),plugin_action_links(), andis_wp_55_or_later() - New: Add new screenshot
- Change: Use default time format if parameter or filter attempts to configure an empty string or non-string value
- Fix: Add support for the ‘T’ timezone format character to the dynamic clock (support for which was removed from Moment.js awhile ago)
- Change: Update bundled Moment.js to v2.29.1
- 2.29.1: https://gist.github.com/marwahaha/cc478ba01a1292ab4bd4e861d164d99b
- 2.29.0: https://gist.github.com/marwahaha/b0111718641a6461800066549957ec14
- 2.28.0: https://gist.github.com/marwahaha/028fd6c2b2470b2804857cfd63c0e94f
- 2.27.0: https://gist.github.com/marwahaha/5100c9c2f42019067b1f6cefc333daa7
- Removed: Dropped support for long-deprecated
'blog_time_format'filter. Use'c2c_blog_time_format'instead. - Change: Switch to use of
wp_add_inline_script()instead ofwp_localize_script() - Change: Add optional
$exitarg toreport_time()to allow not exiting after outputting the time - Change: Improve some inline documentation
- Change: Improve documentation and formatting in readme.txt
- Change: Note compatibility through WP 5.7+
- Change: Update URLs to PHP documentation for datetime formatting
- Change: Update copyright date (2021)
- Unit tests:
- Change: Restructure unit test directories and files into
tests/top-level directory- Change: Move
bin/intotests/ - Change: Move
tests/bootstrap.phpintotests/phpunit/ - Change: In bootstrap, store path to plugin file constant so its value can be used within that file and in test file
- Change: Move
tests/*.phpintotests/phpunit/tests/ - Change: Remove ‘test-‘ prefix from unit test files
- Change: Rename
phpunit.xmltophpunit.xml.distper best practices
- Change: Move
- New: Add tests for
enqueue_js(),report_time(),admin_bar_menu()
- Change: Restructure unit test directories and files into
- New: Add a few more possible TODO items
3.6.2 (2020-06-11)
- Change: Update Moment.js to v2.26.0
- 2.26.0: https://gist.github.com/marwahaha/0725c40740560854a849b096ea7b7590
- 2.25.3: https://github.com/moment/moment/blob/develop/CHANGELOG.md#2253
- 2.25.2: https://github.com/moment/moment/blob/develop/CHANGELOG.md#2252
- 2.25.1: https://github.com/moment/moment/blob/develop/CHANGELOG.md#2251
- 2.25.0: https://gist.github.com/ichernev/6148e64df2427e455b10ce6a18de1a65
- Change: Remove
is_wp_login()since it is no longer necessary - Change: Remove redundant check in
enqueue_js()that is already performed inshow_in_toolbar_for_user() - New: Add TODO.md and move existing TODO list from top of main plugin file into it
- Change: Note compatibility through WP 5.4+
- Change: Update links to coffee2code.com to be HTTPS
- Change: Add an FAQ and tweak docs in readme.txt
- Unit tests:
- New: Add tests for
display_time() - Change: Add more tests for
get_time_format() - Change: Use HTTPS for link to WP SVN repository in bin script for configuring unit tests (and delete commented-out code)
- Change: Remove unnecessary unregistering of hooks in
tearDown()
- New: Add tests for
Full changelog is available in CHANGELOG.md.